Résumé :
The banking sector has evolved in information technology for their internal and external business operations. In effect, user acceptance of internet banking is considered as one of the most fundamental issue in banking sector.
In order to identify which factors affect user intention to adopt internet banking, this study develops an amalgamated model based on technology and social psychological literature. The research model was empirically tested using 398 responses from customers of commercial banks. Data was analyzed using structural equation modeling (SEM). The results of this study provided theoretical and empirical support for newly developed
integrated model. Importance performance matrix analysis (IPMA) revealed that assurance is the most influential factor among all others to determine user’s intention to adopt internet banking. These findings provide valuable insight to marketers and managers to understand customer behavior towards adoption of technology, especially in emerging e-payment domain. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that investigates internet banking adoption issues with integrated technology model (UTAUT & E-SQ) in South Asia.
Finally the study calls for researchers to use current integrated model in other e-commerce domains such as online shopping websites to establish the external validity of the model.
Conclusion :
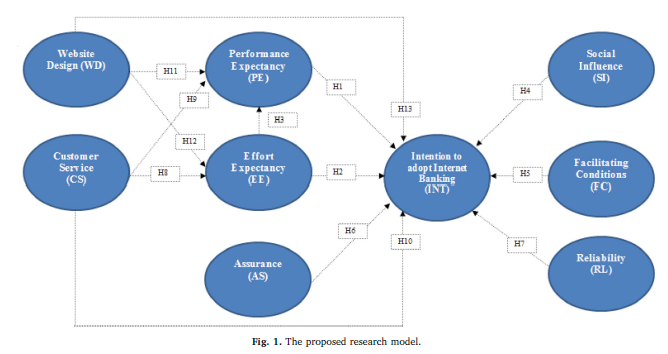
The current study proposed an integrated model UTAUT & E-SQ to investigate user behaviors towards adoption of internet banking. In line with study objectives, the proposed integrated model has direct and positive impact on user intention. This study identified determinants of user beliefs in internet banking adoption context such as website design,
assurance customer service, reliability, performance expectancy, effort expectancy, social influence, and facilitating condition. The results of the structural equation modeling revealed that both website design and customer service have significant influence on performance
expectancy and effort expectancy. Previous studies have claimed that performance expectancy and effort expectancy are the most important determinants to accept internet banking. Therefore, a little has been discussed about the antecedents of performance expectancy and effort expectancy. This study has revealed that website design and customer service are the key factors that enhance users performance expectancy
and effort expectancy towards use of internet banking technology.
These findings demonstrated the success of the proposed integrated model in achieving the objectives of the current study. The findings emanating from current research suggested that there is the need for future research. First, this study integrates UTAUT model with e-service quality to understand user intention towards adoption of internet banking. Therefore, several beneficial areas remain to be explored in other online technology acceptance to investigate customer behavior in online shopping. Second, this study has used intention to adopt as dependent variable to measure the acceptance of internet banking, consistent with prior research Chaouali et al. [51]; Morosan and DeFranco [45]. Therefore, future research may be conducted with actual usage of internet banking instead of intention to adopt. Furthermore, prospect exists for future studies to examine how the newly integrated (UTAUT+E-SQ) model affect the relationship of the constructs put across in this study in other cultural settings. Thus, applying this model to other Asian countries might be interesting.
Bibliographie :
[1] H. Hoehle, E. Scornavacca, S. Huff, Three decades of research on consumer adoption
and utilization of electronic banking channels: a literature analysis, Decis.
Support Syst. 54 (1) (2012) 122–132.
[2] S. Rahi, M.A. Ghani, A structural equation modeling (SEM-AMOS) for investigating
brand loyalty and customer’s intention towards adoption of internet banking, Paper
Presented at the Economic and Social Development (Book of Proceedings), 29th
International Scientific Conference on Economic and Social, 2018.
[3] A.A. Alalwan, A.M. Baabdullah, N.P. Rana, K. Tamilmani, Y.K. Dwivedi, Examining
adoption of mobile internet in Saudi Arabia: extending TAM with perceived enjoyment,
innovativeness and trust, Technol. Soc. 55 (2018) 100–110.
[4] M. Xue, L.M. Hitt, P.-y. Chen, Determinants and outcomes of internet banking
adoption, Manag. Sci. 57 (2) (2011) 291–307.
[5] M. Wang, S. Cho, T. Denton, The impact of personalization and compatibility with
past experience on e-banking usage, Int. J. Bank Mark. 35 (1) (2017).
[6] C. Martins, T. Oliveira, A. Popovič, Understanding the Internet banking adoption: a
unified theory of acceptance and use of technology and perceived risk application,
Int. J. Inf. Manag. 34 (1) (2014) 1–13.
[7] S. Rahi, M.A. Ghani, Customer’s perception of public relation in E-commerce and its
impact on E-loyalty with brand image and switching cost, J. Internet Bank.
Commer. 21 (3) (2016).
[8] M.A. Ghani, S. Rahi, N.M. Yasin, F.M. Alnaser, Adoption of internet banking: extending
the role of technology acceptance model (TAM) with E-customer service
and customer satisfaction, World Appl. Sci. J. 35 (9) (2017) 1918–1929.
[9] S. Rahi, M.A. Ghani, Investigating the role of E-service quality and brand image in
internet banking acceptance context with structural equation modeling (SEM-PLS),
Paper Presented at the Economic and Social Development (Book of Proceedings),
30th International Scientific Conference on Economic and Social, 2018.
[10] R. Samar, M.Y. Norjaya, M.A. Feras, Measuring the role of website design, assurance,
customer service and brand image towards customer loyalty and intention to
adopt interent banking, J. Internet Bank. Commer. 22 (S8) (2017).
[11] S. Samar, M. Ghani, F. Alnaser, Predicting customer’s intentions to use internet
banking: the role of technology acceptance model (TAM) in e-banking, Manag. Sci.
Lett. 7 (11) (2017) 513–524.
[12] K. Al-Qeisi, C. Dennis, E. Alamanos, C. Jayawardhena, Website design quality and
usage behavior: unified theory of acceptance and use of technology, J. Bus. Res. 67
(11) (2014) 2282–2290.
[13] C.-M. Chiu, E.T. Wang, Understanding Web-based learning continuance intention:
the role of subjective task value, Inf. Manag. 45 (3) (2008) 194–201.
[14] J.T. Marchewka, C. Liu, K. Kostiwa, An application of the UTAUT model for understanding
student perceptions using course management software, Commun.
IIMA 7 (2) (2007) 93.
[15] T. Oliveira, M. Thomas, G. Baptista, F. Campos, Mobile payment: understanding the
determinants of customer adoption and intention to recommend the technology,
Comput. Hum. Behav. 61 (2016) 404–414.
[16] F.D. Davis, R.P. Bagozzi, P.R. Warshaw, Extrinsic and intrinsic motivation to use
computers in the workplace1, J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 22 (14) (1992) 1111–1132.
[17] S. Taylor, P. Todd, Assessing IT usage: the role of prior experience, MIS Q. (1995)
561–570.
[18] R.L. Thompson, C.A. Higgins, J.M. Howell, Personal computing: toward a conceptual
model of utilization, MIS Q. (1991) 125–143.
[19] G.C. Moore, I. Benbasat, Integrating Diffusion of Innovations and Theory of
Reasoned Action Models to Predict Utilization of Information Technology by End-
Users Diffusion and Adoption of Information Technology, Springer, 1996, pp. 132–146.
[20] D.R. Compeau, C.A. Higgins, Computer self-efficacy: development of a measure and
initial test, MIS Q. (1995) 189–211.
[21] V. Venkatesh, M.G. Morris, G.B. Davis, F.D. Davis, User acceptance of information
technology: toward a unified view, MIS Q. (2003) 425–478.
[22] S. Rahi, M. Ghani, F. Alnaser, A. Ngah, Investigating the role of unified theory of
acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT) in internet banking adoption context,
Manag. Sci. Lett. 8 (3) (2018) 173–186.
[23] S. Rahi, M.A. Ghani, A.H. Ngah, A structural equation model for evaluating user’s
intention to adopt internet banking and intention to recommend technology,
Accounting 4 (4) (2018) 129–170, https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ac.2018.3.002.
[24] A. Alalwan, Y. Dwivedi, M. Williams, Examining factors affecting customer intention
and adoption of Internet banking in Jordan, Paper Presented at the Proceedings
of United Kingdom Academy of Information Systems UKAIS Conference, 2014.
[25] T. Zhou, Y. Lu, B. Wang, Integrating TTF and UTAUT to explain mobile banking
user adoption, Comput. Hum. Behav. 26 (4) (2010) 760–767.
[26] A. Parasuraman, V.A. Zeithaml, A. Malhotra, ES-QUAL a multiple-item scale for
assessing electronic service quality, J. Serv. Res. 7 (3) (2005) 213–233.
[27] M. Blut, E-service quality: development of a hierarchical model, J. Retail. 92 (4)
(2016) 500–517.
[28] E. Cristobal, C. Flavián, M. Guinalíu, Perceived e-service quality (PeSQ)
Measurement validation and effects on consumer satisfaction and web site loyalty,
Manag. Serv. Qual.: Int. J. 17 (3) (2007) 317–340.
[29] C.-T.B. Ho, W.-C. Lin, Measuring the service quality of internet banking: scale development
and validation, Eur. Bus. Rev. 22 (1) (2010) 5–24.
[30] S. Rahi, M. Ghani, F. Muhamad, Inspecting the role of intention to trust and online
purchase in developing countries, J. Socialomics 6 (1) (2017), https://doi.org/10.
41.72/2167-0358.1000191.
[31] S. Rahi, M.A. Ghani, F.M. Alnaser, The influence of E-customer services and perceived
value on brand loyalty of banks and internet banking adoption: a structural
equation model (SEM), J. Internet Bank. Commer. 22 (1) (2017) 1–18.
[32] M. Wolfinbarger, M.C. Gilly, eTailQ: dimensionalizing, measuring and predicting
etail quality, J. Retail. 79 (3) (2003) 183–198.
[33] B.B. Holloway, S.E. Beatty, Satisfiers and dissatisfiers in the online environment: a
critical incident assessment, J. Serv. Res. 10 (4) (2008) 347–364.
[34] A.M. Aladwani, P.C. Palvia, Developing and validating an instrument for measuring
user-perceived web quality, Inf. Manag. 39 (6) (2002) 467–476.
[35] S.J. Barnes, R.T. Vidgen, An integrative approach to the assessment of e-commerce
quality, J. Electron. Commer. Res. 3 (3) (2002) 114–127.
[36] E.T. Loiacono, R.T. Watson, D.L. Goodhue, WebQual: a measure of website quality,
Market. Theor. Appl. 13 (3) (2002) 432–438.
[37] Z. Yang, X. Fang, Online service quality dimensions and their relationships with
satisfaction: a content analysis of customer reviews of securities brokerage services,
Int. J. Serv. Ind. Manag. 15 (3) (2004) 302–326.
[38] H.H. Bauer, T. Falk, M. Hammerschmidt, eTransQual: a transaction process-based
approach for capturing service quality in online shopping, J. Bus. Res. 59 (7) (2006)
866–875.
[39] F. Alnaser, M. Ghani, S. Rahi, Service quality in Islamic banks: the role of PAKSERV
model, customer satisfaction and customer loyalty, Accounting 4 (2) (2018) 63–72.
[40] C. Liu, K.P. Arnett, Exploring the factors associated with Web site success in the
context of electronic commerce, Inf. Manag. 38 (1) (2000) 23–33.
[41] M. Long, C. McMellon, Exploring the determinants of retail service quality on the
Internet, J. Serv. Mark. 18 (1) (2004) 78–90.
[42] F. Alnaser, M. Ghani, S. Rahi, The impact of SERVQUAL model and subjective
norms on customer’s satisfaction and customer loyalty in islamic banks: a cultural
context, Int. J. Econ. Manag. Sci. 6 (5) (2017) 455.
[43] Y.-C. Shen, C.-Y. Huang, C.-H. Chu, C.-T. Hsu, A benefit–cost perspective of the
consumer adoption of the mobile banking system, Behav. Inf. Technol. 29 (5)
(2010) 497–511.
[44] J.D. Jackson, Y.Y. Mun, J.S. Park, An empirical test of three mediation models for
the relationship between personal innovativeness and user acceptance of technology,
Inf. Manag. 50 (4) (2013) 154–161.
[45] C. Morosan, A. DeFranco, It’s about time: revisiting UTAUT2 to examine consumers’
intentions to use NFC mobile payments in hotels, Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 53 (2016)
17–29.
[46] E. AbuShanab, J.M. Pearson, A.J. Setterstrom, Internet banking and customers’
acceptance in Jordan: the unified model’s perspective, Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 26
(1) (2010) 23.
[47] Y.S. Foon, B.C.Y. Fah, Internet banking adoption in Kuala Lumpur: an application of
UTAUT model, Int. J. Bus. Manag. 6 (4) (2011) 161–167.
[48] F. Shahzad, G. Xiu, M. Shahbaz, Organizational culture and innovation performance
in Pakistan’s software industry, Technol. Soc. 51 (2017) 66–73.
[49] C.L. Miltgen, A. Popovič, T. Oliveira, Determinants of end-user acceptance of biometrics:
integrating the “Big 3” of technology acceptance with privacy context,
Decis. Support Syst. 56 (2013) 103–114.
[50] M. Riffai, K. Grant, D. Edgar, Big TAM in Oman: exploring the promise of on-line
banking, its adoption by customers and the challenges of banking in Oman, Int. J.
Inf. Manag. 32 (3) (2012) 239–250.
[51] W. Chaouali, I.B. Yahia, N. Souiden, The interplay of counter-conformity motivation,
social influence, and trust in customers’ intention to adopt Internet banking
services: the case of an emerging country, J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 28 (2016)
209–218.
[52] G.C. Moore, I. Benbasat, Development of an instrument to measure the perceptions
of adopting an information technology innovation, Inf. Syst. Res. 2 (3) (1991)
192–222.
[53] F. Alnaser, M. Ghani, S. Rahi, M. Mansour, H. Abed, Determinants of customer
loyalty: the role of service quality, customer satisfaction and bank image of islamic
banks in Palestine, Int. J. Econ. Manag. Sci. 6 (461) (2017) 2.
[54] M. Groß, Mobile shopping loyalty: the salient moderating role of normative and
functional compatibility beliefs, Technol. Soc. 55 (2018) 146–159.
[55] S.-J. Hong, J.Y. Thong, J.-Y. Moon, K.-Y. Tam, Understanding the behavior of
mobile data services consumers, Inf. Syst. Front. 10 (4) (2008) 431–445.
[56] F.M.I. Alnaser, M.A. Ghani, S. Rahi, M. Mansour, H. Abed, The influence of services
marketing Mix (7 Ps.) and subjective norms on customer’s satisfaction in islamic
banks of Palestine, Eur. J. Bus. Manag. 9 (27) (2017).
[57] V.A. Zeithaml, Service excellence in electronic channels, Manag. Serv. Qual.: Int. J.
12 (3) (2002) 135–139.
[58] S.I. Swaid, R.T. Wigand, Key dimensions of e-commerce service quality and its relationships
to satisfaction and loyalty, BLED 2007 Proceedings, 29 2007.
[59] S.-M. Kuoppamäki, Digital participation in service environments among senior electricity consumers in Finland, Technol. Soc. 55 (2018) 111–118.
[60] G.J. Udo, K.K. Bagchi, P.J. Kirs, An assessment of customers’e-service quality perception,
satisfaction and intention, Int. J. Inf. Manag. 30 (6) (2010) 481–492.
[61] H. Li, C. Kuo, M.G. Rusell, The impact of perceived channel utilities, shopping orientations,
and demographics on the consumer’s online buying behavior, J.
Computer-Mediated Commun. 5 (2) (1999).
[62] V. Swaminathan, E. Lepkowska-White, B.P. Rao, Browsers or buyers in cyberspace?
An investigation of factors influencing electronic exchange, J. Computer-Mediated
Commun. 5 (2) (1999) 0-0.
[63] M. Wolfinbarger, M.C. Gilly, Shopping online for freedom, control, and fun, Calif.
Manag. Rev. 43 (2) (2001) 34–55.
[64] J. Hulland, H. Baumgartner, K.M. Smith, Marketing survey research best practices:
evidence and recommendations from a review of JAMS articles, J. Acad. Mark. Sci.
(2017) 1–17.
[65] S. Rahi, Research design and methods: a systematic review of research paradigms,
sampling issues and instruments development, Int. J. Econ. Manag. Sci. 6 (2)
(2017) 1–5.
[66] J. Rowley, Designing and using research questionnaires, Manag. Res. Rev. 37 (3)
(2014) 308–330.
[67] P.M. Podsakoff, S.B. MacKenzie, J.-Y. Lee, N.P. Podsakoff, Common method biases
in behavioral research: a critical review of the literature and recommended remedies,
J. Appl. Psychol. 88 (5) (2003) 879.
[68] P.M. Podsakoff, W.H. Bommer, N.P. Podsakoff, S.B. MacKenzie, Relationships between
leader reward and punishment behavior and subordinate attitudes, perceptions,
and behaviors: a meta-analytic review of existing and new research, Organ.
Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 99 (2) (2006) 113–142.
[69] C.M. Ringle, S. Wende, J.-M. Becker, SmartPLS 3, Boenningstedt: SmartPLS GmbH,
2015.
[70] J.F. Hair, W.C. Black, B.J. Babin, R.E. Anderson, R.L. Tatham, Multivariate Data
Analysis 7, (2010).
[71] C. Fornell, D.F. Larcker, Structural equation models with unobservable variables
and measurement error: algebra and statistics, J. Mark. Res. (1981) 382–388.
[72] W.W. Chin, Commentary: Issues and Opinion on Structural Equation Modeling,
JSTOR, 1998.
[73] J. Henseler, C.M. Ringle, R.R. Sinkovics, The Use of Partial Least Squares Path
Modeling in International Marketing New challenges to International Marketing,
Emerald Group Publishing Limited, 2009, pp. 277–319.
[74] J.F. Hair Jr., G.T.M. Hult, C. Ringle, M. Sarstedt, A Primer on Partial Least Squares
Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM), Sage Publications, 2016.
[75] J. Henseler, C.M. Ringle, M. Sarstedt, A new criterion for assessing discriminant
validity in variance-based structural equation modeling, Acad. Mark. Sci. J. 43 (1)
(2015) 115.
[76] R. Kline, Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling, third ed., Guilford
Press, New York, 2011.
[77] A.H. Gold, A.H.S. Arvind Malhotra, Knowledge management: an organizational
capabilities perspective, J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 18 (1) (2001) 185–214.
[78] N. Kock, G. Lynn, Lateral Collinearity and Misleading Results in Variance-Based
SEM: an Illustration and Recommendations, (2012).
[79] F. Hair Jr., M. Sarstedt, L. Hopkins, V.G. Kuppelwieser, Partial least squares
structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) an emerging tool in business research, Eur.
Bus. Rev. 26 (2) (2014) 106–121.
[80] J. Cohen, Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioural Sciences, Lawrence
Earlbaum Associates, Hillside. NJ, 1988.
[81] S. Rahi, M. Abd. Ghani, Does gamified elements influence on user’s intention to
adopt and intention to recommend internet banking? Int. J. Inf. Learn. Technol.
(2018), https://doi.org/10.1108/IJILT-05-2018-0045 0(0), null.
[82] S. Rahi, Moderating role of brand image with relation to internet banking and
customer loyalty: a case of branchless banking, J. Internet Bank. Commer. 20 (3)
(2015) 1.
[83] H.H. Bauer, M. Hammerschmidt, T. Falk, Measuring the quality of e-banking portals,
Int. J. Bank Mark. 23 (2) (2005) 153–175.
[84] S. Rahi, Impact of customer value, public relations perception and brand image on
customer loyalty in services sector of Pakistan, Arabian J. Bus. Manag. Rev. S 2
(2016) 2.
[85] A.G. Mazuri, R. Samar, M.Y. Norjaya, M.A. Feras, Adoption of internet banking:
extending the role of technology acceptance model (TAM) with E-customer service
and customer satisfaction, World Appl. Sci. J. 35 (9) (2017).
[87] R. Samar, A.G. Mazuri, Internet banking, customer perceived value and loyalty: the
role of switching costs, J. Account. Mark. 5 (4) (2016).
[88] R. Samar, A.G. Mazuri, Does gamified elements influence on user’s intention to
adopt internet banking with integration of UTAUT and General Self-Confidence?
Int. J. Bus. Excell. (2019), https://doi.org/10.1504/IJBEX.2019.10016706 0(0).
[89] R. Samar, A.G. Mazuri, Integration of DeLone & McLean and Self-Determination
Theory in internet banking continuance intention context, Int. J. Account. Inf.
Manag. 27 (3) (2019).
